ITAPS
Petascale Technologies
Research | Scaling Results | PHASTA Scaling | FMDB iMesh Implementation | Mesh Adapt | Zoltan Partitioning | Mesquite Mesh Quality | FronTier parallel scaling |
FMDB iMesh Implementation: Scaling Unstructured Mesh Solvers
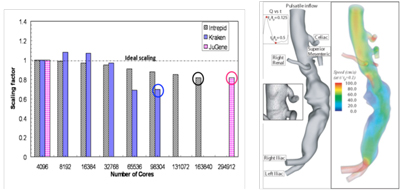
A prerequisite to supporting unstructured mesh operations and adaptive simulations on petascale computers is ensuring that the unstructured mesh solvers scale on these machines. ITAPS team members are involved with the development of such solvers based on implicit methods and unstructured, adapted meshes. This challenging but important class of methods allows for efficient solution of many interesting real-world problems that are otherwise prohibitively expensive to consider with methods using structured grids (mesh grows too large) and/or explicit methods (time step becomes too small). Strong scaling of a method based on unstructured, implicit and adaptive techniques not only enables the solution of extremely large problems but also allows for significant compression in the solution-time for a fixed size problem. Achieving strong scaling on leadership class computing facilities requires advanced interoperable software tools designed specifically to meet the needs of different domain-specific simulations. Table 2 illustrates the parallel efficiency of PHASTA, a parallel, unstructured and implicit flow solver developed at RPI on up to O(100,000) cores of IBM BG and Cray XT systems. PHASTA uses ITAPS technologies including FMDB and the MeshAdapt service for refinement on up to 16K processors and iMeshP and iZoltan to partition the resulting meshes into 128K parts for distribution to the full machine for the analysis step. Near-perfect (linear) strong scaling of the analysis step over multiple doublings of cores can be clearly seen on various systems with a slight decrease in parallel efficiency on the largest core counts due to the fact that computational load per core becomes insignificant (for a fixed-size problem).
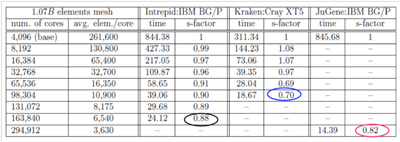
Three large supercomputers have been used and shown to achieve full system scalability with over 70-80 percent efficiency for a blood flow application using PHASTA on up to 288K cores (see the bar graph and table).